Sexual Health Expert
Abnormal Penile Discharge
Penile discharge discharge occurs when fluid leaks from your penis. Both the thickness and color (milky white, greenish, or yellow) of the discharge may vary. The discharge may result from an infection, including a Sexually Transmitted Infection (STI).
Penile discharge is a common symptom of many sexually transmitted diseases (STDs), including gonorrhea and chlamydia, other things can cause it as well. Urethritis is the term used to refer to inflammation of the urethra due to any cause, which is often accompanied by penis discharge.
Penis discharge can be accompanied by bloody or pink-colored urine (hematuria), itching, rash, redness, or swelling. Penis discharge can be extremely uncomfortable and create difficulty with daily living, sexual relations, and urination.

Ruling out an STD
If you’ve ever had any type of sexual contact, it’s important to rule out an STD as a potential cause of your discharge. This can be done with simple urine and blood tests.
Gonorrhea and chlamydia are two of the most common causes of penile discharge. They require treatment with prescription antibiotics. Keep in mind that STDs don’t just result from penetrative intercourse. You can contract an STD by receiving oral sex and engaging in nonintercourse activities.Some STDs don’t cause symptoms immediately.
This means you could still have an STD, even if you haven’t had any sexual contact in months. STDs can cause long-term complications, so it’s important to treat them. This also reduces your risk for transmitting an infection to others.
Common STDs in Men
Gonorrhea

-
Gonorrhea is the most common cause of STD type of penile discharge that any sexually active person can be affected
-
Symptoms include burning during urination, yellow or green discharge, and pain in the testicles.
-
Keep in mind. If left untreated, gonorrhea can increase a person’s chances of getting HIV.
-
More men are affected by Gonorrhea than women. If left untreated,it causes severe health problem.
-
Treatment. Gonorrhea is usually treated with a regimen of two medications, or dual therapy.
Non Gonorrhea Caused of STD
The term non-gonococcal urethritis (NGU) is used when the condition is not caused by the gonorrhoea. NGU is sometimes referred to as non-specific urethritis (NSU) when no cause can be found.
Several different organisms can cause the syndrome:


Mycoplasma
Genitalium
(up to 25%)



Ureaplasma
Urealyticum/
Parvum (15-25%)
Herpes Simplex (HSV)
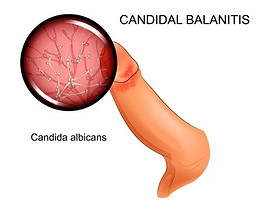
Yeast
Non-STD Caused of Penile Discharge

Urinary Tract Infection (UTI)
How to Diagnose Penile Discharge?
The colour and consistency of the discharge only does not help to distinguish NSU from gonococcal urethritis. There are few tests that can be done to diagnose the causes of penile discharge, and all may be carried out to make sure the diagnosis is correct. The infecting organism can be identified from these samples.
The tests are:
-
Urethral swab test : A sample of fluid is taken from your urethra using a swab, which is like a small cotton bud. The swab may have a small cotton tip at the end to swab the discharge
-
Urine test : To make the test more accurate, you’ll be asked not to pee for at least 2 hours before providing a urine sample or ‘first catch’ urine sample (urine taken from when you first begin to pass urine).
-
Blood test : Blood test is usually taken to rule out other type of STD such as HIV, Syphilis, Herpes and Hepatitis.

What Are The Potential Complications of Penile Discharge?
Because penis discharge can be due to serious diseases, failure to seek treatment can result in serious complications and permanent damage. Once the underlying cause is diagnosed, it is important for you to follow the treatment plan that you and your health care professional design specifically for you to reduce the risk of potential complications including:
-
Difficulty with or inability to retract the foreskin
-
Scarring and narrowing of the opening of the penis
-
Scarring of the penis
-
Spread of cancer
-
Spread of infection which can cause infertility, chronic pelvic pain,chronic prostatitis and others
How To Treat Penile Discharge?
Depending on the cause, a course of antibiotics is usually the first point of defence for penile discharge:
Gonorrhoea
CDC recommends a single dose of 250mg of intramuscular ceftriaxone plus 1g of oral azithromycin.
Non Gonorrhea Caused of STD
Chlamydia trachomatis / Ureaplasma / Mycoplasma / :
Doxycycline 100mg twice daily for seven days or a single dose of azithromycin 1g as a single dose.
Trichomonas Vaginalis:
Metronidazole two times a day for seven days.
Herpes Simplex Virus:
Valacyclovir: 1000 mg orally twice daily for 7 days
You and your partner should wait at least 1-2 weeks after you both finish treatment to resume sexual activity. Your doctor may advise you to follow up for testing after 6weeks (known as a ‘test of cure’) to make sure the infection is completely gone.